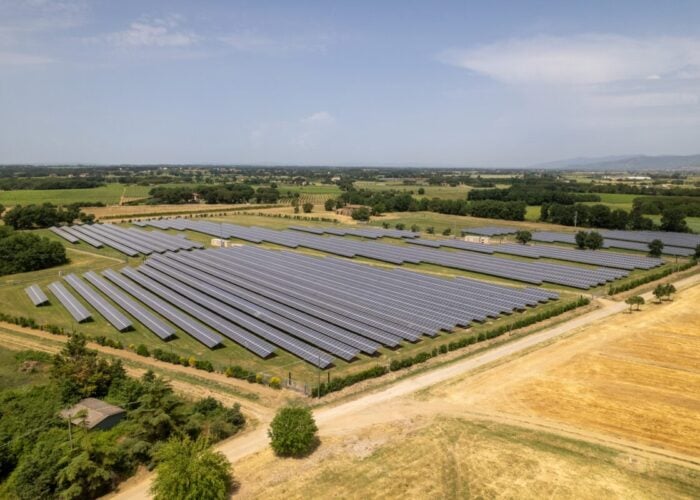
Only one per cent of land in Italy is suitable for ground-mounted solar PV projects without limitations, according to analysis company McKinsey.
In its new report Land: A crucial resource for the energy transition, McKinsey looked at the land restrictions for EU countries – with the cases of Germany’s onshore wind and Italy’s solar PV – in order to add all the renewables capacity targeted in the REPowerEU strategy, which is set at 600GW by 2030 for solar PV alone.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
France, Germany and Italy alone – who would represent nearly half of the EU’s renewables installations by 2030 – could require an additional 23,000 to 35,000 square kilometres of land. This is nearly the size of Belgium.
What affects the most land availability in Europe is due to regulations, which can even vary within a country as some of the rules are established at a regional level.
In Italy’s case, land available for solar PV is restricted due to regulatory limitations on the use of cropland, which accounts for almost a third of the total land area and 80% of the total available land after technical constraints.
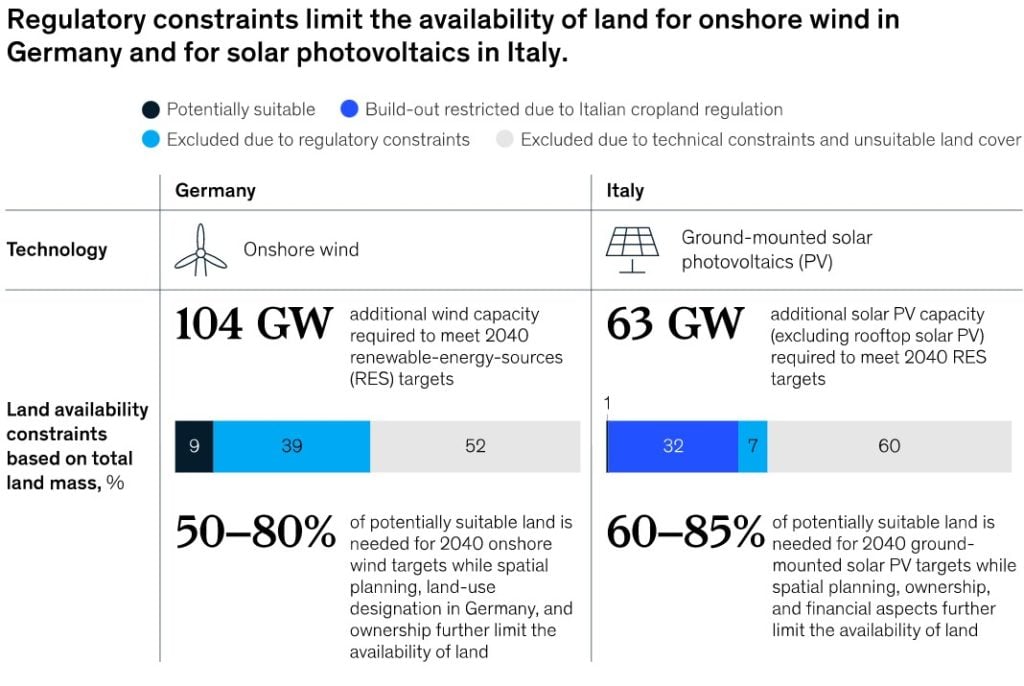
For the country to add 63GW of new solar capacity by 2040 it would require up to 85% of available land, according to McKinsey. A solution to reduce the restrictions on solar PV would be the increased share of land for crops and solar PV, such as agrivoltaics.
“Increasing the European Union’s RES [renewable energy sources] capacity at the rate needed to achieve its stated objectives will require substantial amounts of land throughout the region, which could be limited in some countries,” says the report.






